Neodymium magnets, known for their exceptional magnetic strength and compact size, are playing an increasingly vital role in advancing space exploration technologies. Their unique properties make them indispensable in both spacecraft propulsion systems and the emerging field of space resource utilization. However, their application in the harsh environment of space also presents significant challenges.
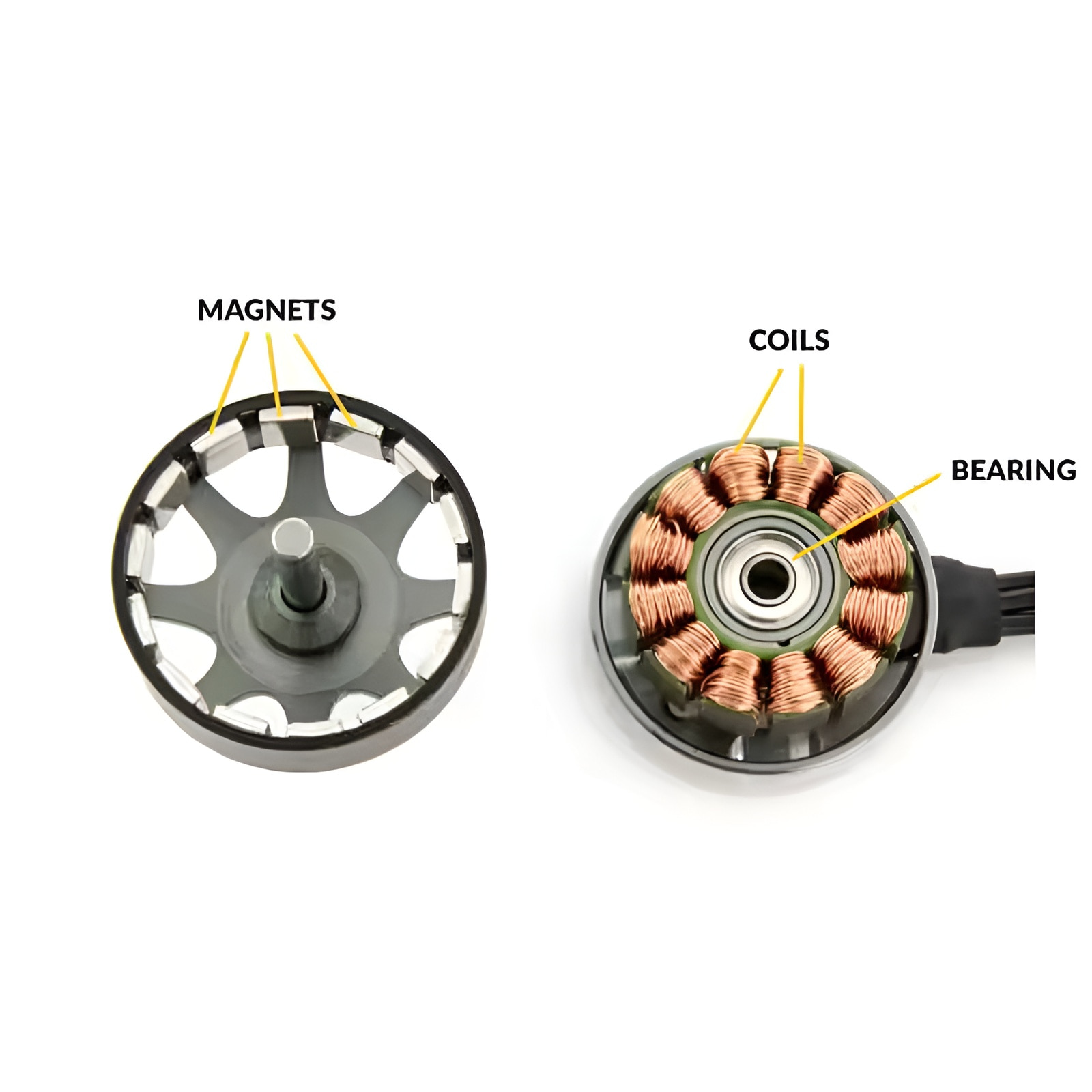
One of the most promising applications of high performance neodymium magnets is in advanced propulsion systems, such as ion and plasma propellers. These systems rely on strong magnetic fields to accelerate charged particles, generating thrust with high efficiency. Neodymium magnets, with their high magnetic energy density, are ideal for creating the compact yet powerful magnetic fields required. For example, in ion propellers, these magnets help confine and direct plasma, enabling spacecraft to achieve higher speeds while consuming less fuel compared to traditional chemical propulsion. This technology is particularly valuable for long-duration missions, such as interplanetary travel, where efficiency is critical.
Another exciting frontier is the use of neodymium magnets in space resource extraction, particularly in asteroid mining. Asteroids are rich in valuable metals like iron, nickel, and rare earth elements. Neodymium magnets can be employed to separate and collect these magnetic materials in the micro gravity environment of space. For instance, magnetic separators equipped with neodymium magnets could efficiently extract iron-rich particles from asteroid weathering layer, paving the way for in-situ resource utilization (ISRU). This capability could reduce the need to transport materials from Earth, significantly lowering the cost and complexity of space missions.
Despite their potential, super quality ndfeb permanent magnets face challenges in space applications. The extreme conditions of space, including high levels of radiation and drastic temperature fluctuations, can affect their performance. Prolonged exposure to cosmic radiation may lead to demagnetization, while temperature variations can alter their magnetic properties. Additionally, the micro gravity environment poses unique engineering challenges in designing systems that can reliably operate with magnetic forces.
To overcome these challenges, ongoing research focuses on developing radiation-resistant coatings and advanced alloys that enhance the durability of neodymium magnets in space. Furthermore, innovations in magnetic system design aim to optimize their performance in micro gravity. As space exploration continues to expand, the role of neodymium magnets is expected to grow, enabling more efficient propulsion, sustainable resource utilization, and groundbreaking discoveries in the cosmos.

In conclusion, powerful neodymium rare earth magnets are a key enabler of modern space exploration, offering solutions to some of the most pressing challenges in propulsion and resource extraction. However, addressing their limitations in space environments will be crucial to unlocking their full potential.