Earthquake resistant engineering has evolved significantly in recent years, incorporating cutting-edge materials and technologies to enhance structural resilience. One such innovation is the application of neodymium magnets, which have emerged as a promising tool for mitigating earthquake-induced damage. These powerful rare earth magnets offer unique properties that can improve energy dissipation, damping mechanisms, and overall structural stability during seismic events.
Magnetic Damping Systems
Neodymium magnets play a crucial role in passive damping systems, which help reduce the amplitude of seismic vibrations. Engineers have developed magnetorheological (MR) dampers, where a fluid infused with iron particles responds to magnetic fields generated by neodymium magnets. By adjusting the magnetic field intensity, the viscosity of the fluid changes, allowing real-time control over damping forces and improving a building’s ability to withstand earthquakes.
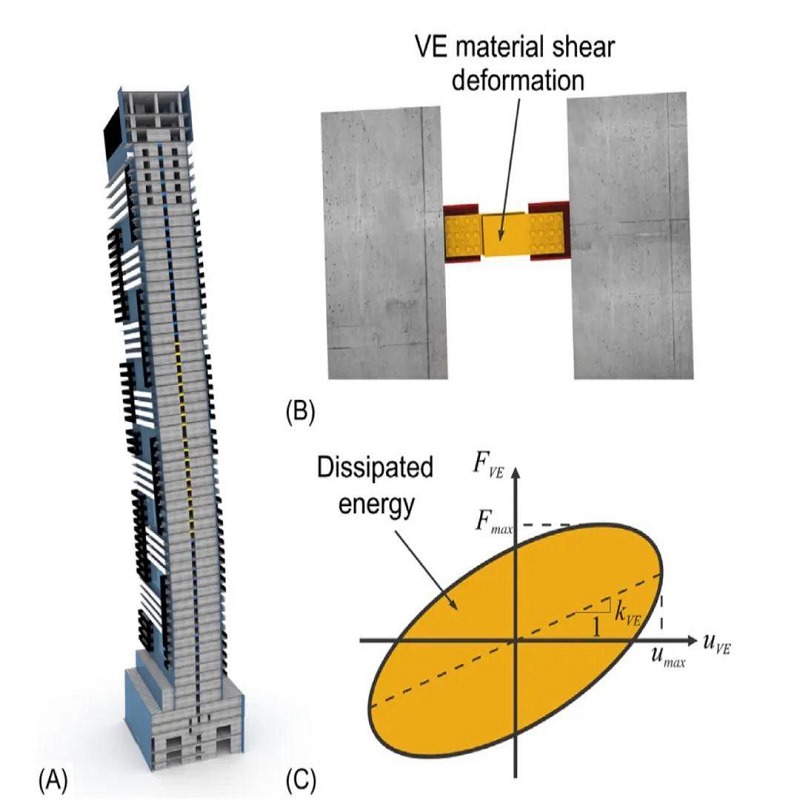
Magnetic Levitation for Base Isolation
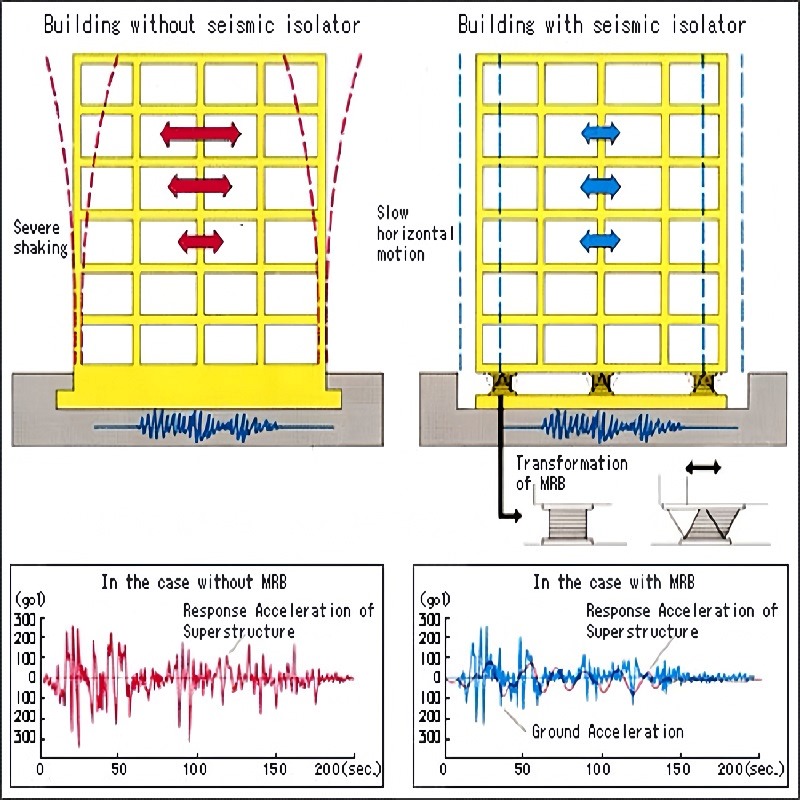
Another innovative application of neodymium magnets in seismic engineering is in base isolation systems. Traditional base isolators rely on rubber and steel layers to absorb ground motion. However, researchers are exploring the use of magnetic levitation, where high performance neodymium magnets create repulsive forces that suspend structures above their foundations. This system significantly reduces the transmission of seismic energy to the building, minimizing structural damage.
Energy Harvesting for Structural Monitoring
Neodymium magnets are also being used for energy harvesting in earthquake-resistant buildings. By converting mechanical vibrations into electrical energy, magnetic induction systems powered by neodymium magnets can supply energy to structural health monitoring devices. These sensors help detect early signs of damage and provide real-time data to engineers, ensuring timely maintenance and safety assessments.
Future Prospects
The use of good quality neodymium magnets in earthquake resistant engineering is still evolving, with ongoing research exploring new ways to enhance earthquake resistance. As technology advances, we can expect more cost-effective and efficient applications, improving the safety and durability of infrastructure in earthquake-prone regions.
